歯並びの傾斜「目のライン」と「本当の水平」の話‐瞳孔線、自然頭位、咬合平面、水平的な審美の基準
矯正治療や審美治療において、「前歯の先端のライン(上顎前歯切縁または咬合平面)」をどこに合わせるか?というのは、実は非常に奥が深く、そして悩ましい問題です。
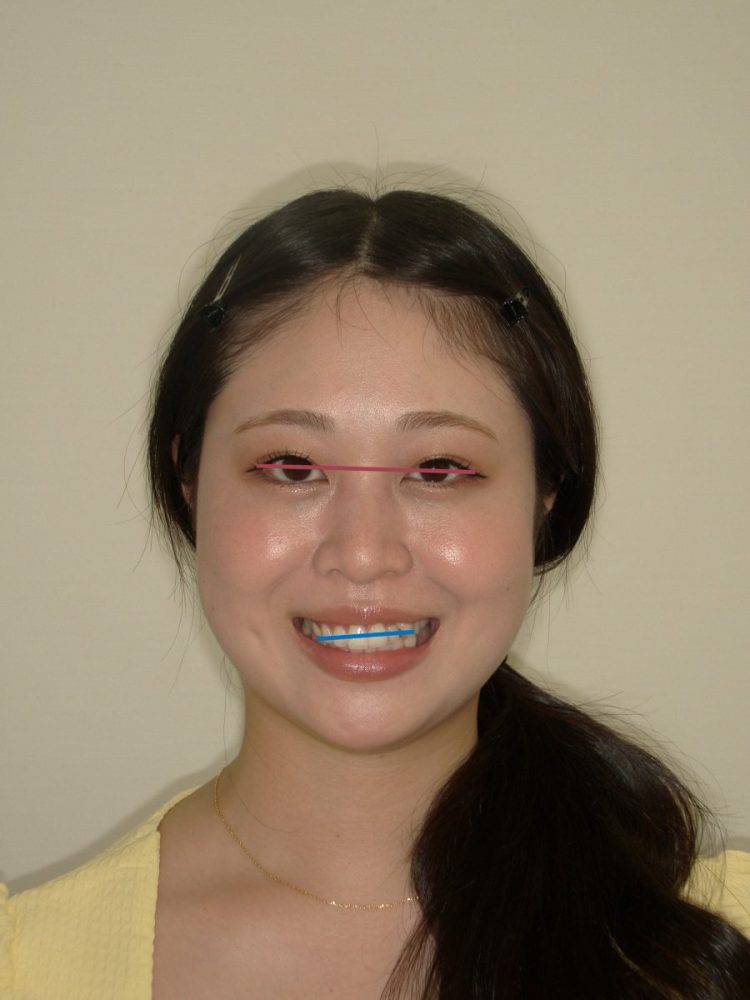
教科書的な正解として長年言われてきたのは、「瞳孔線(両目の瞳孔を結んだ線)と平行にする」というものです。
「目と平行なら美しく見える」——これは直感的にもわかりやすいですよね。
しかし、最新の研究データを見ていくと、この「常識」が必ずしも正解ではないことがわかってきました。
美しい口元の基準とされるE-lineが70年前の基準であることは以前のコラムで書きました。今回は、少しマニアックですが、美しいスマイルを作るための「基準線」についてお話しします。
「目のライン」は実は水平ではない?
いきなり衝撃的なデータですが、2025年の最新の研究(Albertini et al.)によると、約半数の人で、瞳孔線と本当の水平線(重力に対する水平)との間に「2度以上のズレ」があることが報告されています。
つまり、人間の顔というのは、元々左右非対称なのが当たり前で、「目の高さが左右で違う」なんてことはザラにあるわけです。
もし、目が右下がりになっている患者さんに対して、「目と平行に」歯並びを作ったらどうなるでしょうか?
顔全体で見ると、歯並びまで右下がりに見えてしまい、患者さんが真っ直ぐ立った時に「あれ?なんか顔が歪んで見える…」という結果になりかねません。
信頼できるのは「自然頭位(NHP)」
そこで、現在の水平的な基準のスタンダードとされるのが「自然頭位(Natural Head Position: NHP)」という基準です。
これは簡単に言うと、「リラックスして遠くを見ている時の頭の位置」のこと。
研究(Madsen et al., 2008 他)によれば、この自然頭位こそが、個人内での再現性が高く、真の水平線(Horizon)に最も近い信頼できる基準であるとされています。
当院でも、ただ写真を撮るだけでなく、患者さんがリラックスして立っている姿勢や、顔全体のバランスを重視して診断を行っていますが、それはこの「真の水平」を見誤らないためでもあります。
「3度」までは許容範囲?人間の目の不思議
では、厳密に水平でなければならないかというと、そうでもありません。人間の感覚というのは案外アバウトで、かつ柔軟です。
審美的な評価に関する研究(Soheilifar et al., 2023 他)では、「咬合平面の傾きが3度以内であれば、多くの人は違和感を覚えない」とされています。
これは一般の方だけでなく、我々歯科医師が見ても同様の傾向があります。
つまり、機械のように0.1度の狂いもなく水平にすることに執着するよりも、その人の顔立ちや、口角の上がり方、そして自然な頭の位置との調和を優先する方が結果として「自然で美しい笑顔」になるのです。
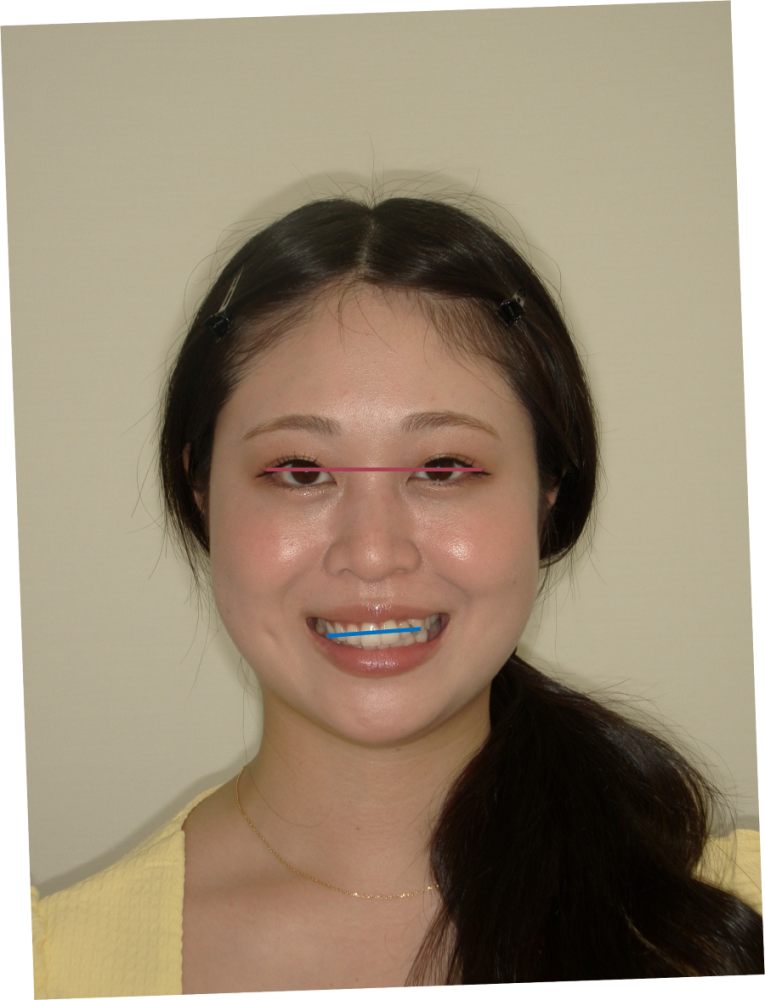

最新機器「フェイススキャナ」を使う際の落とし穴
当院では、RAYFaceなどの最新のフェイススキャナを用いて、顔の3Dデータを活用した診断を行っています。しかし、ここでも「基準をどこに置くか」という運用上の注意が非常に重要になります。
多くのデジタルソフトは、顔のデータを読み込む際、自動的に「両目(瞳孔線)」を水平に合わせて表示しようとします。 もし、この自動補正をそのまま信じて治療計画を立ててしまったらどうなるでしょうか?
先ほどの研究結果の通り、半数の人は目のライン自体が傾いています。つまり、「画面上では真っ直ぐに見えるけれど、実際の患者さんの顔では傾いている」というズレが生じてしまうのです。
「機器」×「診断力」がカギ
フェイススキャナを使う際にはこのポイントの理解がとても重要で、AI任せの自動整列ではなく、患者さんの「自然頭位(NHP)」を正しく理解して比較検討する必要があります。
- 患者さんがリラックスして立った時の姿勢はどうなっているか?
- 顔全体の正中線(真ん中のライン)はどう通っているか?
こういったアナログな観察眼と、デジタルの正確な計測を組み合わせることで初めて、誤差のない「本当の美しさ」をデザインできるのです。
結論:木(口元だけ)を見ず、森(顔全体)を見る
- 第一基準は「自然頭位(NHP)」:リラックスした姿勢での本当の水平を重視する。
- デジタル機器も使い手が重要:スキャンデータもNHPに合わせて正しく運用する。
- 完璧を目指しすぎない:3度以内の傾きなら、むしろ自然に見えることもある。
「鏡で見ると歯が斜めに見える気がする」と悩んでいる方も、実はそれが「顔全体のバランス」の中では正解であるケースも少なくありません。
また、成人矯正では咬合平面の傾斜や上下歯列の正中不一致は骨格のズレが原因であることが殆どです。
上下歯列の正中を骨格からズレた位置に設定し、無理に歯列正中一致させるが長期安定するかは疑問ですね。
当院では、RAYFaceなどの最新機器を駆使しつつ、数値だけに頼らない「人の目」による診断を大切にしています。自分のスマイルラインが気になる方は、ぜひ一度ご相談ください。
エビデンスメモ
Albertini, G., Bechelli, D., Capusotto, A., Porta, M., Burelli, M., & Lanis, A. (2025). Observational Analysis of Discrepancy Between the Interpupillary Line and the Horizon Line in Natural Head Position.. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry, 0 0, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.11607/prd.7501
Kois, J., Kois, D., Zeitler, J., & Martin, J. (2021). Digital to Analog Facially Generated Interchangeable Facebow Transfer: Capturing a Standardized Reference Position.. Journal of prosthodontics : official journal of the American College of Prosthodontists. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopr.13437
Moorrees, C. (1994). Natural head position–a revival.. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics, 105 5, 512-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-5406(94)70014-1
Madsen, D., Sampson, W., & Townsend, G. (2008). Craniofacial reference plane variation and natural head position.. European journal of orthodontics, 30 5, 532-40. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjn031
Chiu, C., & Clark, R. (1991). Reproducibility of natural head position.. Journal of dentistry, 19 2, 130-1. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-5712(91)90111-b
Moorrees, C., & Kean, M. (1958). Natural head position, a basic consideration in the interpretation of cephalometric radiographs. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 16, 213-234. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.1330160206
Soheilifar, S., Nouri, M., Safari, M., Soheilifar, S., Soheilifar, S., Nowzari, M., Youssefinia, S., & Naghdi, N. (2023). Perception of laypersons, orthodontists, and oral and maxillofacial surgeons about the transverse occlusal plane.. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2023.02.011
Lundström, F., & Lundström, A. (1992). Natural head position as a basis for cephalometric analysis.. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics, 101 3, 244-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/0889-5406(92)70093-p
Sangalli, L., Dalessandri, D., Bonetti, S., Mandelli, G., Visconti, L., & Savoldi, F. (2022). Proposed parameters of optimal central incisor positioning in orthodontic treatment planning: A systematic review. Korean Journal of Orthodontics, 52, 53 – 65. https://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2022.52.1.53
Silva, B., Tortora, S., Stanley, K., Mahn, G., Coachman, C., & Mahn, E. (2019). Layperson’s preference of the transverse occlusal plane in asymmetric facial model.. Journal of esthetic and restorative dentistry : official publication of the American Academy of Esthetic Dentistry … [et al.]. https://doi.org/10.1111/jerd.12526
Masoud, M., Bansal, N., Castillo, J., Manosudprasit, A., Allareddy, V., Haghi, A., Hawkins, H., & Otárola-Castillo, E. (2016). 3D dentofacial photogrammetry reference values: a novel approach to orthodontic diagnosis. European Journal of Orthodontics, 39, 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjw055
Lee, K., Kang, J., Lee, H., & Kim, S. (2021). Ideal Reference Lines for Assessment of Facial Asymmetry in Rhinoplasty Patients. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 46, 321-328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02565-0
Marcotte, M. (2009). Head posture and dentofacial proportions.. The Angle orthodontist, 51 3, 208-13. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(1981)051<0208:hpadp>2.0.co;2
Chen, C., Lai, S., Tseng, Y., & Lee, K. (2008). Simple technique to achieve a natural head position for cephalography.. The British journal of oral & maxillofacial surgery, 46 8, 677-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.03.022
Bass, N. (1991). The aesthetic analysis of the face.. European journal of orthodontics, 13 5, 343-50. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/13.5.343
Chen, M., Lum, J., Yong, C., Lai, W., & Wong, R. (2023). Placing the maxilla in the most aesthetic sagittal position: validation of several reference lines in relation to the forehead shape.. International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2023.11.003
Solow, B., & Tallgren, A. (1971). Natural head position in standing subjects.. Acta odontologica Scandinavica, 29 5, 591-607. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016357109026337
Yurdakurban, E., Duran, G., & Görgülü, S. (2021). Evaluation of an Automated Approach for Facial Midline Detection and Asymmetry Assessment: A Preliminary Study.. Orthodontics & craniofacial research. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12539
Dvortsin, D., Ye, Q., Pruim, G., Dijkstra, P., & Ren, Y. (2011). Reliability of the integrated radiograph-photograph method to obtain natural head position in cephalometric diagnosis.. The Angle orthodontist, 81 5, 889-94. https://doi.org/10.2319/010411-2.1
Margossian, P., Laborde, G., Koubi, S., Tardivo, D., & Magne, P. (2021). Determination of Facial References for Esthetic Restorative Treatment.. The International journal of periodontics & restorative dentistry, 41 1, 113-119. https://doi.org/10.11607/prd.4642
Lundström, A., Forsberg, C., Westergren, H., & Lundström, F. (1991). A comparison between estimated and registered natural head posture.. European journal of orthodontics, 13 1, 59-64. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/13.1.59
Petričević, N., Čelebić, A., Ćelić, R., & Baučić-Božić, M. (2006). Natural head position and inclination of craniofacial planes.. The International journal of prosthodontics, 19 3, 279-80.
Ferrario, V., Sforza, C., Germano, D., Dalloca, L., & Miani, A. (1994). Head posture and cephalometric analyses: An integrated photographic/radiographic technique.. American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics, 106 3, 257-264. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-5406(94)70045-1
Bass, N. (2003). Measurement of the profile angle and the aesthetic analysis of the facial profile.. Journal of orthodontics, 30 1, 3-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ortho/30.1.3
Yin, A., Dong, Y., Zhang, X., Song, B., & Bai, S. (2024). A new method to orient a 3-dimensional facial model to natural head position: a preliminary report on accuracy and reproducibility.. Journal of stomatology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, 101980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jormas.2024.101980
Lundström, A., Lundström, F., Lebret, L., & Moorrees, C. (1995). Natural head position and natural head orientation: basic considerations in cephalometric analysis and research.. European journal of orthodontics, 17 2, 111-20. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/17.2.111
Finn, S., Silver, M., Canary, B., Kantarcı, A., Allareddy, V., Katebi, N., & Masoud, M. (2018). A modified Steiner’s analysis that does not require radiographic exposure of the cranial base. Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research, 22, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12250
Olivares, A., Vicente, A., Jacobo, C., Molina, S., Rodriguez, A., & Bravo, L. (2013). Canting of the occlusal plane: Perceptions of dental professionals and laypersons. Medicina Oral, Patología Oral y Cirugía Bucal, 18, e516 – e520. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.18335
Carvalho, A., Costa, L., Martins, J., Manso, M., Gavinha, S., Herrero-Climent, M., Ríos-Carrasco, B., Falcão, C., & Ribeiro, P. (2021). Aesthetic Preference in the Transverse Orientation of the Occlusal Plane in Rehabilitation: Perspective of Laypeople and Dentists. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212258
Wilson, P., Namano, D., Behrend, M., Harcourt, O., , F., & , D. (2000). Angular asymmetries of the human face.. The International journal of prosthodontics, 13 1, 41-6.
Revilla‐León, M., Meyer, M., Barrington, J., Sones, A., Umorin, M., Taleghani, M., & Zandinejad, A. (2019). Perception of occlusal plane that is nonparallel to interpupillary and commissural lines but with the maxillary dental midline ideally positioned.. The Journal of prosthetic dentistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.01.023
監修者

中嶋 亮 | Ryo Nakajima
日本大学松戸歯学部卒業後、同大学大学院にて歯科矯正学を専攻し修了。大学病院での研鑽を経て、2012年より「銀座矯正歯科」に勤務し、数多くの裏側矯正や複雑な症例に携わる。2021年に院長、現在は理事長として診療にあたる。見た目の美しさと咬合機能の両立を重視し、特に舌側矯正やデジタル技術を活用した精密治療に注力。患者一人ひとりの生活背景に寄り添い、長期的な健康と自然な笑顔を引き出すことを理念としている。
【略歴】
- 1998年 富山県立富山中部高等学校卒業
- 1998〜2004年 日本大学松戸歯学部
- 2004〜2008年 日本大学大学院(歯科矯正学専攻)
- 2008〜2012年 日本大学松戸歯学部 歯科矯正学講座 助手(専任扱)
- 2012〜2020年 医療社団法人真美会 銀座矯正歯科 アシスタントドクター
- 2013〜2014年 ニューヨーク大学CDEP 矯正学修了
- 2014〜2018年 日本大学松戸歯学部 顎顔面外科学講座 兼任講師
- 2014〜2015年 カリフォルニア州立大学LA校CDEP 矯正学修了
- 2019〜2023年 日本大学松戸歯学部 歯科矯正学講座 兼任講師
- 2021年〜 医療社団法人真美会 銀座矯正歯科 院長
- 2022年〜 日本デジタル矯正歯科学会 理事・学術担当
- 2023年〜 日本大学松戸歯学部 歯科矯正学講座 クリニカルアドバイザー
- 2023年〜 Digital Dentistry Society Ambassador (Japan)
- 2023年〜 日本大学松戸歯学部 歯科矯正学講座 同門会副会長
- 2023年〜 RayFace (RayDent, Korea) Key Opinion Leader
- 2024年〜 医療法人社団真美会 理事長
【主な所属学会】
- ・日本矯正歯科学会(認定医)
- ・International Congres of Oral Implantrogists (ICOI) インプラント矯正認定医
- ・Digital Dentistry Society 日本アンバサダー
- ・先進歯科画像研究会(ADI) 歯科用CT認定医
- ・厚生労働省認定 歯科臨床研修指導医
- ・日本美容外科学会(JSAPS) 関連会員
- ・Orthopaedia and Solutions マネージャー
- ・(株)YDM 矯正器材アドバイザー
- ・ABO Journal Club 主宰
- ・Cutting Edge of Digital Orthodontics 主宰
- ・BiTechOrtho代表
- ・Orthodontics Institute Japan代表
【論文・学会発表】
- ・加速矯正とアライナー治療による治療期間のコントロール ザ・クインテッセンス2022年11月号
- ・進化するデジタル歯科技術Extra モディファイドコルチコトミー法とSureSmileによる矯正治療 日本歯科評論 81(8)=946:2021.8
- ・進化するデジタル歯科技術 : 3Dプリンターは臨床をどう変革するか(4)矯正治療における3Dプリンターの臨床応用 日本歯科評論 81(4)=942:2021.4
- ・矯正用光重合型レジン系接着システムの接着性能 接着歯学2013年31巻4号P159-166
- ・歯科矯正学における3D診断および治療計画(翻訳) クインテッセンス出版
- ・基礎から学ぶデジタル時代の矯正入門(翻訳統括) クインテッセンス出版
- ・矯正歯科治療のためのコルチコトミー(翻訳)
- ・Effects of… cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2008 Apr;43(2):168-73.
- ・Evaluation…lary tuberosity. J World Fed Orthod. 2022 Jun;11(3):69-74.
- ・T-helper 1…essive orthodontic forces. Oral Dis. 2012 May;18(4):375-88
- ・IL-8 and M…s in periodontal tissues. Oral Dis. 2011 Jul;17(5):489-98.
- ・Effects of…dontal ligament cells. Inflamm Res. 2011 Feb;60(2):187-94.
- ・Effects of…igament cells. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2009 Nov;12(4):282-8.
- ・Levels of …cells in vitro. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2006 May;9(2):63-70.
- ・日本デジタル歯科学会招待講演(2024年)
- ・東北矯正歯科学会招待講演(2025年)
- ・加速矯正による治療期間短縮のコンセプト クインテッセンス出版
- ・Levels of …cells in vitro. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2006 May;9(2):63-70.
